TOXICITY EFFECT OF RADIOGRAPHIC DEVELOPER EFFLUENT ON GIANT AFRICAN SNAIL (ACHATINA FULICA)
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: The decline in the population of snails, a source of protein of people living in the high forest zone due to environmental pollution and the hazard caused by the disposal of radiographic developer effluent into streams, bushes or forests and public sewer systems makes the assessment of the effect on giant African snails (Achatina fulica) from environmental pollution due to radiographic developer effluent very important.
Materials and Methods: Ninety 5 months old, 12 months old and 24 months old giant African snails were randomly divided into 6 groups of 15 snails for each age group based on the dose of developer effluent to be administered. One group from each age group was designated the control and the remaining, the experimental group. Range finding test was performed at effluent concentrations of 100 %, 50 %, 25 %, 12.5 %, 6.25 %, 3.125 %, 1.6 % and 0 % (control) in 150 ml of distilled water. The effluent solution was administered on the feed and soil of the experimental snails only.
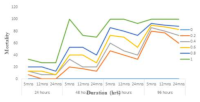
Results: Behavioural changes occurred between 0.2 – 1.0 % concentration and mortality at 24 – 96 hours exposure to the effluent solutions. The percentage (%) mortality of the giant African snails increased as the effluent concentration increased from 0.2 - 1.0 % and at increased exposure time of 24 – 96 hours. The estimated 96 hours LD50 for the 5, 12 and 24 months old giant African snails were 0.20 0.23, 0.23 0.25 and 0.30 0.26 respectively.
Conclusion: Radiographic developer effluent is harmful to the giant African snails, with the % mortality increasing with increase in concentration and exposure time to the developer effluent. Legislation is recommended to ensure safe disposal of radiographic developer effluents into the Nigerian environment considering the importance of giant African snails (Achatina fulica) to the ecosystem and the economy.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
All articles in JRRS are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
How to Cite
References
[1] Okpeze CN, Omole AJ, Ajayi FT and Adebowal E. A. Effects of feeding adult snails Stylosanths guinanesis or Lablab purpureus as substitute for paw paw leaf. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2007; 6: 1959 – 1962.
[2] Baba KM and Adeleke MT. Profitability of Snail Production in Osun State. Journal of Agriculture and Food Sciences, Nigeria, 2006; 4 (20): 147 – 155.
[3] Ademosun AA and Omidiji MO. The nutrient value of African giant land snail (Archachatina marginata). Journal of Animal Protection
Research, 1999; 8 (2): 876 – 877.
[4] Agbogidi MO and Okonta BC. Reducing poverty through snail farming in Nigeria. Agriculture and Biology Journal of North America, 2011; 2 (1): 169-172.
[5] Efarmspro: Snail Farming and Management. URL www.efarmspro.com th . Accessed on 29 of December 2016.
[6] Ues K, Piaia L and Schweickardt M. The use of advanced oxidation processes in the degradation of waste developer and x-ray fixer. Proceedings of the XVI Meeting of the Southern Region Chemistry 13 - 15 November 2008, Blumenau, SC, Brazil.
[7] Marcos A, Oswaldo SN, Jefson MA and José B. Evaluation of radiographic waste management in dental offices and radiology clinics of São Luís (MA), RSBO, 2012; 9 (3): 260 - 265.
[8] Briggs GG and Henderson IF. Some factors affecting the toxicity of poisons to the slug Deracerous reticulatum (Muller) (Pulmonata
Limacidae). Crop Prot, 1987; (6): 342-346.
[9] Chiaghanam NO, Egbe NO, Nzotta CC, Ollawa CU and Akpan ER. Assessment of the toxicity of radiographic developer effluent on catfish Heterobranchus longifilis. Global Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 2012; 18 (1&2): 105-107.
[10] Ugwu AC, Dimkpa U, Agba ON, Eteudo AN, Anikeh, LC, Maduka SO, Uchefuna RC, NjokuOji NN and Okonkwo OC. Splenotoxic effect of radiographic developer effluent on Wister rats. International Journal of Research in Medical Science, 2016; 4 (5): 1625 - 1631.
[11] Ugwu AC, Dimkpa U, Fotso D, Eteudo AN, Maduka SO, Njoku-Oji NN et al. Cardiotoxic assessment of radiographic developer effluent in Wistar rats. Journal of Adv. Med. Pharm Sci., 2016; 6 (4): 1-11.
[12] USEPA. The toxicity of 3400 chemicals to fish part 2: The toxicity of 1085 chemicals to fish. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, Office of Toxic Substances (EPA), 1987; 560/6-87-002.
[13] Priya A, Trupti S and Mira R. Insecticidal activity of different solvent extracts of Zanthoxylum Rhetsa (ROXB) DC. against Tribolum Castaneum Herbst. World Journal of Pharmaceutical and life Sciences, 2016; 2(4): 230 - 239.
[14] Sachs L. A handbook of techniques: Applied Statistics, 2nd Edition. Springer-verlas, New York. (1984).
[15] Seilbergeld E K, Holmberg B, Högberg J, Johanson G, Djuric D, Jakubowski M, Telišman S et al. Toxicology: Tools and Approaches,
Encyclopaedia of Occupational Health and Safety, 4th Edition. International Labour Organization. (2012).
[16] Mohammed A (2013) Why are Early Life Stages of Aquatic Organisms More Sensitive to Toxicants than Adults? New Insights into Toxicity and Drug Testing, Intech Open. (2013). DOI: 10.5772/55187.
[17] Guerra R. Ecotoxicological and chemical evaluation of Phenolic compounds industrial effluents. Chemosphere, 2001; 44 (8): 1737 – 1747.
[18] Chen H, Yao J, Wang F, Choi M M, Bramanti E and Zaray G (2009) Study on the toxic effects of diphenol compounds on soil microbial activity by a combination of methods. Journal of Hazardous Materials 167(1-3): 846 – 851.
[19] Sabuncuoglu BT, Kocaturk PA, Yaman O, Kavas GO and Tekelioglu M. Effects of subacute boric acid administration on rat kidney tissue. Clinical Toxicology, 2006; 44 (3): 249-253.
[20] HU Q, Li S, Qiao E, Tang Z, Erhui J, Jin G and Gu Y. Effects of Boron on Structure and Antioxidative Activities of Spleen in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem Res. 2014; 158: 73 - 80.
[21] Ouano EA. Assessment of the quality and type of land-based pollutant discharges into the marine and coastal environment, Training manual, 1988; 54-55.