A SURVEY OF DIAGNOSTIC X-RAY ROOM DESIGN AND SHIELDING INTEGRITY OF LEAD APRONS IN A STATE IN NORTH EASTERN NIGERIA
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: X-ray facility design and shielding integrity is meant to optimize radiation safety of patients, staff and the general public.
Objectives: To determine the conformity to x-ray room design standards and the functional efficacy of lead aprons in the surveyed facilities.
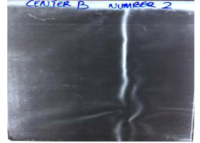
Materials and Method: The survey was conducted in six radio diagnostic centers in Gombe State Nigeria, labeled A to F for anonymity. The building layout of the radiology departments was sketched to show the dimensions (L x B x H) and adjoining structures. Data sheets were also used to record information about radio-diagnostic facility. Lead aprons were inspected for defects by physical observation and by x-ray exposure.
Results: The x-ray room dimension of the six radio diagnostic centers with A(24m2 ), B (14.8 m2 ), C (30 m2 ), D (36 m2 ), E (21.2 m2 ) and F (25 m2 ). All the walls of radio-diagnostic room of facility A, B, C and D were lined with 2 mm lead equivalent, whereas E and F were not. About 7 (38.8%) of lead aprons inspected were defective, while 11 (61.1%) were not defective.
Conclusion: There are compromises noted in the design of facility B and majority of the lead aprons inspected showed good functional efficacy.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
All articles in JRRS are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.