EVALUATION OF THE CHALLENGES OF THE ADOPTION OF VIRTUAL REALITY TECHNOLOGY IN RADIOGRAPHY TRAINING IN SOME SELECTED SCHOOLS IN THE SOUTHEAST, NIGERIA.
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the challenges associated with implementing virtual reality technology in radiography training and education in selected schools in the southeast region.
Materials and Methods: A cross-sectional survey design was adopted which included 14 respondents involved in radiography training and education across four universities in the south-east, Nigeria. The instrument used for data collection in this study was a comprehensive online questionnaire. The questionnaire measured the demographic information of the respondents, level of adoption and implementation of VR in their institutions, challenges in VR adoption, strategies, and solutions to these challenges. These questions were tested for internal consistency using Cronbach’s alpha reliability test and a coefficient value of 0.562 got.
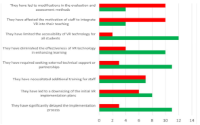
Results: The results of this study showed that financial constraints (n=8, 57%) and lack of technical support or expertise (n=8, 57%) are major challenges in adopting VR technology in radiography education and training. Seven respondents (50%) agreed that technical difficulties are another major challenge in adopting VR technology in radiography education and training. Challenges of virtual reality technology were believed to have an overall negative impact on the adoption of virtual reality technology in radiography instruction and training (n=10, 71%). The study also indicated how these challenges affected the efficacy and standard of radiography education, with 10 respondents (71%) claiming these challenges to be detrimental.
Conclusion: The adoption of Virtual Reality (VR) technology in radiography training and education faces significant challenges in southeast, Nigeria.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
All articles in JRRS are published under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). This permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
How to Cite
References
1. Von Itzstein GS, Billinghurst M, Smith RT, Thomas BH. Augmented Reality Entertainment: Taking Gaming Out of the Box. 2017. Doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-08234-9_81-1
2. Kaufmann H, Schmalstieg D. Designing immersive virtual reality for geometry education. In: Ieee virtual reality conference (vr 2006) [Internet]. IEEE; 2006 [cited 2024, Jan20]. p.51–8. Available from:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1667626
3. Gradl S, Eskofier BM, Eskofier D, Mutschler C, Otto S. Virtual and augmented reality in sports: an
overview and acceptance study. In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct [Internet]. Heidelberg Germany: ACM; 2016 [cited 2024 Jan 20]. p. 885–8. Available from: doi:10.1145/2968219.2968572
4. Hollins, M., Deery, H., & Ku, M. (2020). Virtual reality and medical training: A review of the evidence. Simulation in Healthcare, 15(3), 189-196.
5. Chen, L., Liu, Q., & Yang, W. (2021). Virtual reality in medical education: A comprehensive review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23(2), e20432.
6. Moro C, Štromberga Z, Raikos A, Stirling A. The effectiveness of virtual and augmented reality in health sciences and medical anatomy. Anatomical Sciences Ed. 2017 Nov;10(6):549–59. Doi: 10.1002/ase.1696
7. Johnston R, Adams T, Smith K. Virtual reality in medical education: A meta-analysis of learning
outcomes. Med Educ Rev. 2020;45(1):23-35.
8. Anderson, C. A., & Bower, M. (2018). The effectiveness of virtual reality in medical education: A systematic review. Medical Education, 52(6), 571-583.
9. Rizzo, A. S., & Koenig, S. T. (2020). Virtual reality and serious games for mental health treatment.
Virtual Reality, 24(1), 103-114.
10. Harris, D. M., Williams, J., & Chang, R. (2019). Barriers to adopting virtual reality in higher education: A review. Educational Technology Research and Development, 67(5), 1431-1450.
11. Schuster, M., Reichenbach, J., & Voss, S. (2022). Overcoming resistance to virtual reality adoption in educational institutions. Journal of Educational Technology, 45(2), 213-226.
12. Flinton DM. Competency based assessment using virtual reality (VERT): is it a realistic possibility? [Internet] [PhD Thesis]. University of East London; 2015 [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://repository.uel.ac.uk/item/8547q
13. Rizzo AA, Koenig ST. Clinical results using virtual reality. J Technol Hum Serv. 2019 ;37(1):51-74.
doi: 10.1080/15228835.2019.1652363..
12. Flinton DM. Competency based assessment using virtual reality (VERT): is it a realistic possibility?
[Internet] [PhD Thesis]. University of East London; 2015 [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://repository.uel.ac.uk/item/8547q
13. Rizzo AA, Koenig ST. Clinical results using virtual reality. J Technol Hum Serv. 2019 ;37(1):51-74.
doi: 10.1080/15228835.2019.1652363..